最近在做抽奖服务端接口,会涉及到抽奖概率的问题,网上查资料找到一个比较好的抽奖概率的算法,Alias Method概率抽奖算法。今天就来分享一下这个算法的C#、PHP以及Java的实现。
举个例子,游戏中玩家推倒了一个boss,会按如下概率掉落物品:10%掉武器 20%掉饰品 30%掉戒指 40%掉披风。现在要给出下一个掉落的物品类型,或者说一个掉落的随机序列,要求符合上述概率。
一般会想到的两种解法
第一种算法,构造一个容量为100(或其他)的数组,将其中10个元素填充为类型1(武器),20个元素填充为类型2(饰品)…构造完毕之后,在1到100之间取随机数rand,取到的array[rand]对应的值,即为随机到的类型。这种方法优点是实现简单,构造完成之后生成随机类型的时间复杂度就是O(1),缺点是精度不够高,占用空间大,尤其是在类型很多的时候。
第二种就是一般的离散算法,通过概率分布构造几个点,[10, 30, 60, 100],没错,后面的值就是前面依次累加的概率之和(是不是像斐波那契数列)。在生成1~100的随机数,看它落在哪个区间,比如50在[30,60]之间,就是类型3。在查找时,可以采用线性查找,或效率更高的二分查找,时间复杂度O(logN)。
这里推荐一个大牛的两篇文章,从数学入手,探讨各种算法实现。《用JavaScript玩转游戏编程(一)掉宝类型概率》 和《实验比较各离散采样算法》 。想深入了解的朋友推荐看看。
参考他的文章中得到两个概念,PDF(密度分布函数)和 CDF(累积分布函数)两种概率分布,分别对应如上两种算法:
| T | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |
| CDF | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 |
1.0 |
好了,现在就来说一下Alias Method(别名方法)
在这里我们不深究他的数学原理(http://www.keithschwarz.com/darts-dice-coins/ 这篇文章里详述了其原理),来看看如何使用和实现。譬如说如上的PDF[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4],将每种概率当做一列,别名算法最终的结果是要构造拼装出一个每一列合都为1的矩形,若每一列最后都要为1,那么要将所有元素都乘以4(概率类型的数量)
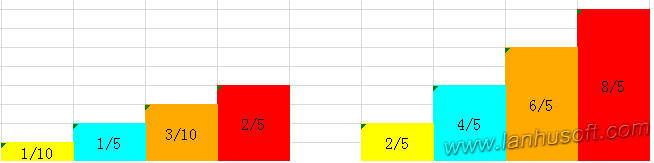
此时会有概率大于1的和小于1的,接下来就是构造出某种算法用大于1的补足小于1的,使每种概率最后都为1,注意,这里要遵循一个限制:每列至多是两种概率的组合。
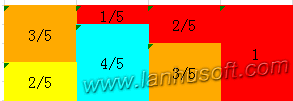
最终,我们得到了两个数组,一个是在下面原始的prob数组[0.4,0.8,0.6,1],另外就是在上面补充的Alias数组,其值代表填充的那一列的序号索引,(如果这一列上不需填充,那么就是NULL),[3,4,4,NULL]。当然,最终的结果可能不止一种,你也可能得到其他结果。
等等,这个问题还没有解决,得到这两个数组之后,随机取其中的一列,比如是第三列,让prob[3]的值与一个随机小数f比较,如果f小于prob[3],那么结果就是3,否则就是Alias[3],即4。
我们可以来简单验证得到的概率是不是正确的,比如随机到第三列的概率是1/4,得到第三列下半部分的概率为1/4*3/5,记得在第一列还有它的一部分,那里的概率为1/4*(1-2/5),两者相加最终的结果还是3/10,符合原来的pdf概率。这种算法初始化较复杂,但生成随机结果的时间复杂度为O(1),是一种性能非常好的算法。
| T | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |
| Alias | 3 | 4 | 4 |
NULL |
一、Alias Method概率抽奖算法的C#实现
- using System;
- using System.Collections;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace Lanhusoft.Core
- {
- public class AliasMethod
- {
- /* The probability and alias tables. */
- private int[] _alias;
- private double[] _probability;
- public AliasMethod(List<Double> probabilities)
- {
- /* Allocate space for the probability and alias tables. */
- _probability = new double[probabilities.Count];
- _alias = new int[probabilities.Count];
- /* Compute the average probability and cache it for later use. */
- double average = 1.0 / probabilities.Count;
- /* Create two stacks to act as worklists as we populate the tables. */
- var small = new Stack<int>();
- var large = new Stack<int>();
- /* Populate the stacks with the input probabilities. */
- for (int i = 0; i < probabilities.Count; ++i)
- {
- /* If the probability is below the average probability, then we add
- * it to the small list; otherwise we add it to the large list.
- */
- if (probabilities[i] >= average)
- large.Push(i);
- else
- small.Push(i);
- }
- /* As a note: in the mathematical specification of the algorithm, we
- * will always exhaust the small list before the big list. However,
- * due to floating point inaccuracies, this is not necessarily true.
- * Consequently, this inner loop (which tries to pair small and large
- * elements) will have to check that both lists aren't empty.
- */
- while (small.Count > 0 && large.Count > 0)
- {
- /* Get the index of the small and the large probabilities. */
- int less = small.Pop();
- int more = large.Pop();
- /* These probabilities have not yet been scaled up to be such that
- * 1/n is given weight 1.0. We do this here instead.
- */
- _probability[less] = probabilities[less] * probabilities.Count;
- _alias[less] = more;
- /* Decrease the probability of the larger one by the appropriate
- * amount.
- */
- probabilities[more] = (probabilities[more] + probabilities[less] - average);
- /* If the new probability is less than the average, add it into the
- * small list; otherwise add it to the large list.
- */
- if (probabilities[more] >= average)
- large.Push(more);
- else
- small.Push(more);
- }
- /* At this point, everything is in one list, which means that the
- * remaining probabilities should all be 1/n. Based on this, set them
- * appropriately. Due to numerical issues, we can't be sure which
- * stack will hold the entries, so we empty both.
- */
- while (small.Count > 0)
- _probability[small.Pop()] = 1.0;
- while (large.Count > 0)
- _probability[large.Pop()] = 1.0;
- }
- /**
- * Samples a value from the underlying distribution.
- *
- * @return A random value sampled from the underlying distribution.
- */
- public int next()
- {
- long tick = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
- var seed = ((int)(tick & 0xffffffffL) | (int)(tick >> 32));
- unchecked
- {
- seed = (seed + Guid.NewGuid().GetHashCode() + new Random().Next(0, 100));
- }
- var random = new Random(seed);
- int column = random.Next(_probability.Length);
- /* Generate a biased coin toss to determine which option to pick. */
- bool coinToss = random.NextDouble() < _probability[column];
- return coinToss ? column : _alias[column];
- }
- }
- }
二、Alias Method概率抽奖算法的PHP实现
- <?php
- class AliasMethod
- {
- private $length;
- private $prob_arr;
- private $alias;
- public function __construct ($pdf)
- {
- $this->length = 0;
- $this->prob_arr = $this->alias = array();
- $this->_init($pdf);
- }
- private function _init($pdf)
- {
- $this->length = count($pdf);
- if($this->length == 0)
- die("pdf is empty");
- if(array_sum($pdf) != 1.0)
- die("pdf sum not equal 1, sum:".array_sum($pdf));
- $small = $large = array();
- $average=1.0/$this->length;
- for ($i=0; $i < $this->length; $i++)
- {
- $pdf[$i] *= $this->length;
- if($pdf[$i] < $average)
- $small[] = $i;
- else
- $large[] = $i;
- }
- while (count($small) != 0 && count($large) != 0)
- {
- $s_index = array_shift($small);
- $l_index = array_shift($large);
- $this->prob_arr[$s_index] = $pdf[$s_index]*$this->length;
- $this->alias[$s_index] = $l_index;
- $pdf[$l_index] += $pdf[$s_index]-$average;
- if($pdf[$l_index] < $average)
- $small[] = $l_index;
- else
- $large[] = $l_index;
- }
- while(!empty($small))
- $this->prob_arr[array_shift($small)] = 1.0;
- while (!empty($large))
- $this->prob_arr[array_shift($large)] = 1.0;
- }
- public function next_rand()
- {
- $column = mt_rand(0, $this->length - 1);
- return mt_rand() / mt_getrandmax() < $this->prob_arr[$column] ? $column : $this->alias[$column];
- }
- }
- ?>
三、Alias Method概率抽奖算法的Java实现
- package com.lanhusoft.rsaapp;
- import android.util.Log;
- import java.util.*;
- import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
- public final class AliasMethod {
- /* The random number generator used to sample from the distribution. */
- private final Random random;
- /* The probability and alias tables. */
- private final int[] alias;
- private final double[] probability;
- /**
- * Constructs a new AliasMethod to sample from a discrete distribution and
- * hand back outcomes based on the probability distribution.
- * <p/>
- * Given as input a list of probabilities corresponding to outcomes 0, 1,
- * ..., n - 1, this constructor creates the probability and alias tables
- * needed to efficiently sample from this distribution.
- *
- * @param probabilities The list of probabilities.
- */
- public AliasMethod(List<Double> probabilities) {
- this(probabilities, new Random());
- }
- /**
- * Constructs a new AliasMethod to sample from a discrete distribution and
- * hand back outcomes based on the probability distribution.
- * <p/>
- * Given as input a list of probabilities corresponding to outcomes 0, 1,
- * ..., n - 1, along with the random number generator that should be used
- * as the underlying generator, this constructor creates the probability
- * and alias tables needed to efficiently sample from this distribution.
- *
- * @param probabilities The list of probabilities.
- * @param random The random number generator
- */
- public AliasMethod(List<Double> probabilities, Random random) {
- /* Begin by doing basic structural checks on the inputs. */
- if (probabilities == null || random == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- if (probabilities.size() == 0)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Probability vector must be nonempty.");
- /* Allocate space for the probability and alias tables. */
- probability = new double[probabilities.size()];
- alias = new int[probabilities.size()];
- /* Store the underlying generator. */
- this.random = random;
- /* Compute the average probability and cache it for later use. */
- final double average = 1.0 / probabilities.size();
- /* Make a copy of the probabilities list, since we will be making
- * changes to it.
- */
- probabilities = new ArrayList<Double>(probabilities);
- /* Create two stacks to act as worklists as we populate the tables. */
- Deque<Integer> small = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
- Deque<Integer> large = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
- /* Populate the stacks with the input probabilities. */
- for (int i = 0; i < probabilities.size(); ++i) {
- /* If the probability is below the average probability, then we add
- * it to the small list; otherwise we add it to the large list.
- */
- if (probabilities.get(i) >= average)
- large.add(i);
- else
- small.add(i);
- }
- /* As a note: in the mathematical specification of the algorithm, we
- * will always exhaust the small list before the big list. However,
- * due to floating point inaccuracies, this is not necessarily true.
- * Consequently, this inner loop (which tries to pair small and large
- * elements) will have to check that both lists aren't empty.
- */
- while (!small.isEmpty() && !large.isEmpty()) {
- /* Get the index of the small and the large probabilities. */
- int less = small.removeLast();
- int more = large.removeLast();
- /* These probabilities have not yet been scaled up to be such that
- * 1/n is given weight 1.0. We do this here instead.
- */
- probability[less] = probabilities.get(less) * probabilities.size();
- alias[less] = more;
- /* Decrease the probability of the larger one by the appropriate
- * amount.
- */
- probabilities.set(more,
- (probabilities.get(more) + probabilities.get(less)) - average);
- /* If the new probability is less than the average, add it into the
- * small list; otherwise add it to the large list.
- */
- if (probabilities.get(more) >= 1.0 / probabilities.size())
- large.add(more);
- else
- small.add(more);
- }
- /* At this point, everything is in one list, which means that the
- * remaining probabilities should all be 1/n. Based on this, set them
- * appropriately. Due to numerical issues, we can't be sure which
- * stack will hold the entries, so we empty both.
- */
- while (!small.isEmpty())
- probability[small.removeLast()] = 1.0;
- while (!large.isEmpty())
- probability[large.removeLast()] = 1.0;
- }
- /**
- * Samples a value from the underlying distribution.
- *
- * @return A random value sampled from the underlying distribution.
- */
- public int next() {
- /* Generate a fair die roll to determine which column to inspect. */
- int column = random.nextInt(probability.length);
- /* Generate a biased coin toss to determine which option to pick. */
- boolean coinToss = random.nextDouble() < probability[column];
- /* Based on the outcome, return either the column or its alias. */
- /* Log.i("1234","column="+column);
- Log.i("1234","coinToss="+coinToss);
- Log.i("1234","alias[column]="+coinToss);*/
- return coinToss ? column : alias[column];
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TreeMap<String, Double> map = new TreeMap<String, Double>();
- map.put("1金币", 0.2);
- map.put("2金币", 0.15);
- map.put("3金币", 0.1);
- map.put("4金币", 0.05);
- map.put("未中奖", 0.5);
- List<Double> list = new ArrayList<Double>(map.values());
- List<String> gifts = new ArrayList<String>(map.keySet());
- AliasMethod method = new AliasMethod(list);
- Map<String, AtomicInteger> resultMap = new HashMap<String, AtomicInteger>();
- for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
- int index = method.next();
- String key = gifts.get(index);
- if (!resultMap.containsKey(key)) {
- resultMap.put(key, new AtomicInteger());
- }
- resultMap.get(key).incrementAndGet();
- }
- for (String key : resultMap.keySet()) {
- System.out.println(key + "==" + resultMap.get(key));
- }
- }
- }
文章转载自:蓝狐软件工作室 » C#&PHP&Java实现Alias Method概率抽奖算法
 架构C
架构C