什么是负载均衡器?
假设有一个分布式系统,该系统由在不同计算机上运行的许多服务组成。但是,当用户数量很大时,通常会为服务创建搭建集群。集群中每个服务实例都在单独一台计算机上运行。此时,出现 “Load Balancer(负载均衡器)”。它有助于在服务器之间平均分配传入流量。
服务器端负载均衡器
传统Load Balancers(例如Nginx、F5)是放置在服务器端的组件。当请求来自 客户端 时,它们将转到负载均衡器,负载均衡器将为请求指定服务器。负载均衡器使用的最简单的算法是随机指定。在这种情况下,大多数负载平衡器是用于控制负载平衡的硬件集成软件。
特点:
- 对客户端不透明,客户端不知道服务器端的服务列表,甚至不知道自己发送请求的目标地址存在负载均衡器。
- 服务器端维护负载均衡服务器,控制负载均衡策略和算法。
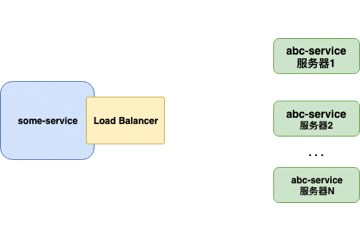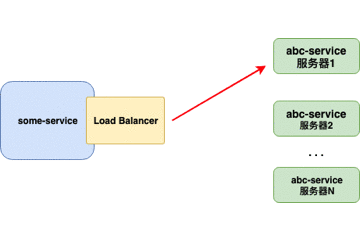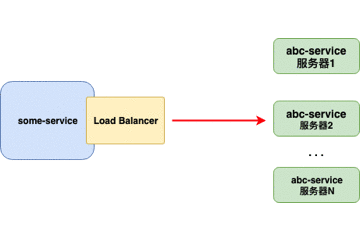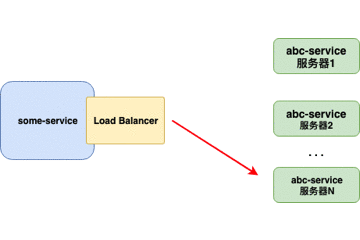
客户端负载均衡器
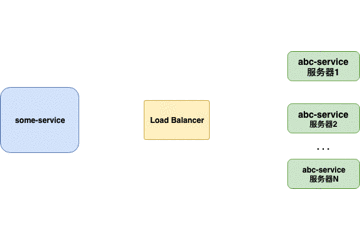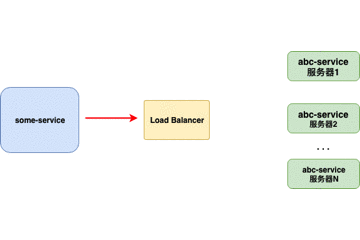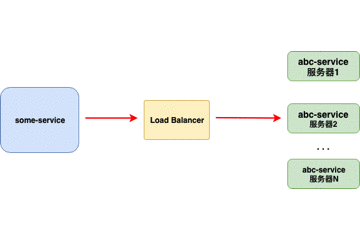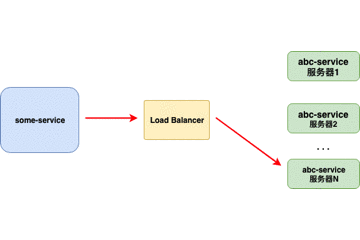
当负载均衡器位于客户端时,客户端得到可用的服务器列表然后按照特定的负载均衡策略,分发请求到不同的服务器 。
特点:
- 对客户端透明,客户端需要知道服务器端的服务列表,需要自行决定请求要发送的目标地址。
- 客户端维护负载均衡服务器,控制负载均衡策略和算法。
- 目前单独提供的客户端实现比较少(Ribbon是其中之一),大部分都是在框架内部自行实现。
Ribbon
简介
Ribbon是Netflix公司开源的一个客户单负载均衡的项目,可以自动与 Eureka 进行交互。它提供下列特性:
- 负载均衡
- 容错
- 以异步和反应式模型执行多协议 (HTTP、TCP、UDP)
- 缓存和批量
Ribbon中的关键组件
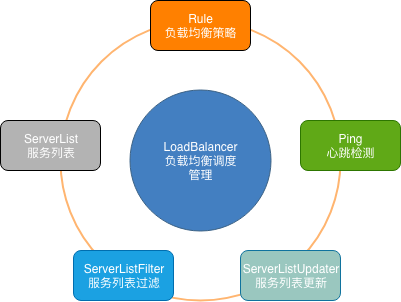
- ServerList:可以响应客户端的特定服务的服务器列表。
- ServerListFilter:可以动态获得的具有所需特征的候选服务器列表的过滤器。
- ServerListUpdater:用于执行动态服务器列表更新。
- Rule:负载均衡策略,用于确定从服务器列表返回哪个服务器。
- Ping:客户端用于快速检查服务器当时是否处于活动状态。
- LoadBalancer:负载均衡器,负责负载均衡调度的管理。
源码分析
LoadBalancerClient
实际应用中,通常将 RestTemplate 和 Ribbon 结合使用,例如:
@Configuration
public class RibbonConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
消费者调用服务接口:
@Service
public class RibbonService {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
public String hi(String name) {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-hi/hi?name="+name,String.class);
}
}
@LoadBalanced,通过源码可以发现这是一个标记注解:
@Target({ ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Qualifier
public @interface LoadBalanced {
}
通过注释可以知道@LoadBalanced注解是用来给RestTemplate做标记,方便我们对RestTemplate添加一个LoadBalancerClient,以实现客户端负载均衡。
自动装载核心配置类
SpringCloud对EurekaServer的封装使得发布一个EurekaServer无比简单,根据自动装载原则可以在spring-cloud-netflix-ribbon-2.2.5.RELEASE.jar下的META-INF目录下找到 spring.factories文件
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonAutoConfiguration
RibbonAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@Conditional(RibbonAutoConfiguration.RibbonClassesConditions.class)
@RibbonClients
@AutoConfigureAfter(
name = "org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration")
@AutoConfigureBefore({ LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class,
AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ RibbonEagerLoadProperties.class,
ServerIntrospectorProperties.class })
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {
}
先决条件
- @ConditionalOnClass:当前环境必须存在这几个类:IClient、RestTemplate、AsyncRestTemplate、Ribbon
- @RibbonClients:这个注解上面已经讲过了。
- @AutoConfigureAfter:负载均衡肯定是要基于注册中心来做的,所以自动装配是在Eureka初始化完毕之后初始化的。
- @AutoConfigureBefore:这里的两个类先不说,保持神秘。
- @EnableConfigurationProperties,两个配置类,其中:
- RibbonEagerLoadProperties类中是关于Ribbon的饥饿加载模式的属性
- ServerIntrospectorProperties类中是关于安全端口的属性
@RibbonClients
@RibbonClients注解使用@Import注解引入了配置类RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE })
@Documented
@Import(RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar.class)
public @interface RibbonClients {
RibbonClient[] value() default {};
Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {};
}
RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar
RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar是一个 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,为配置了注册了对应 RibbonClientSpecification 的 BeanDefinition。
public class RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//RibbonClients 注解解析, 遍历注册所有 RibbonClient 配置类的
Map<String, Object> attrs = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(RibbonClients.class.getName(), true);
if (attrs != null && attrs.containsKey("value")) {
AnnotationAttributes[] clients = (AnnotationAttributes[]) attrs.get("value");
for (AnnotationAttributes client : clients) {
registerClientConfiguration(registry, getClientName(client),
client.get("configuration"));
}
}
// 全局默认配置
if (attrs != null && attrs.containsKey("defaultConfiguration")) {
String name;
if (metadata.hasEnclosingClass()) {
name = "default." + metadata.getEnclosingClassName();
}
else {
name = "default." + metadata.getClassName();
}
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attrs.get("defaultConfiguration"));
}
// 单个 RibbonClient 的解析,注册对应配置类的 BD
Map<String, Object> client = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(RibbonClient.class.getName(), true);
String name = getClientName(client);
if (name != null) {
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name, client.get("configuration"));
}
}
// 注册类型为 RibbonClientSpecification
private void registerClientConfiguration(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object name,
Object configuration) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(RibbonClientSpecification.class);
builder.addConstructorArgValue(name);
builder.addConstructorArgValue(configuration);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(name + ".RibbonClientSpecification",
builder.getBeanDefinition());
}
}
- 首先会判断是否存在注解@RibbonClients,注意,这里可是多了一个s的
然后判断@RibbonClients注解上是否存在属性value和defaultConfiguration,如果存在的话分别注册他们。 - 接着最后才是处理@RibbonClient注解
这里我们就可以猜测RibbonClientConfigurationRegistrar这个类应该是可以同时处理这两个注解的,观察一下@RibbonClients注解的源码发现它确实是引入的也是这个类
这两个注解的区别应该也可以猜测出来,单数和双数 - 观察最后注册的代码,可以看到最后注册bean的类型都是RibbonClientSpecification。
RibbonAutoConfiguration
该类由 自动装配 加载,对应于 OpenFeign 的 FeignContext,所有 RibbonContext 的 上下文 由 SpringClientFactory 创建和管理
// 扫描的所有 RibbonClientSpecification
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 将所有的 RibbonClientSpecification 交给 SpringClientFactory
* 由 SpringClientFactory 创建和管理对应的 RibbonClient 上下文
*/
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {
SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();
factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return factory;
}
这跟 FeignContext 的原理一模一样,因此不再过多解读,RibbonClient 对应的 上下文 创建与管理由 SpringClientFactory 实现。
SpringClientFactory,每一个微服务在都会调用多个微服务,而调用各个微服务的配置可能是不一样的,所以就需要这个创建客户端负载均衡器的工厂类,它可以为每一个ribbon客户端生成不同的Spring上下文,而观察这个类的configurations属性也验证了这一点
同时,RibbonAutoConfiguration 还创建了 LoadBalancerClient 的实例,为 RibbonLoadBalancerClient
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
public LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient() {
return new RibbonLoadBalancerClient(springClientFactory());
}
RestTemplateCustomizer RestTemplate定制器
//Ribbon的http请求配置
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(HttpRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnRibbonRestClient
protected static class RibbonClientHttpRequestFactoryConfiguration {
@Autowired
private SpringClientFactory springClientFactory;
//RestTemplate定制器
@Bean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(
final RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory) {
return restTemplate -> restTemplate
.setRequestFactory(ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory);
}
//注册RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ,听过它来创建ClientHttpRequest用来发http请求的,
//后续Ribbon执行流程中会用到ClientHttpRequest
@Bean
public RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory ribbonClientHttpRequestFactory() {
return new RibbonClientHttpRequestFactory(this.springClientFactory);
}
}
上方虽然看了Ribbon的自动装配功能,但是好像离真相还有一些距离,这是因为虽然Ribbon准备好了,但是负载均衡还没看呢。SpringCloud把负载均衡相关的自动配置放在了spring-cloud-commons包下,负载均衡的配置类是LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigureBefore注解会加载LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
//必须存在RestTemplate类
@ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class)
//必须存在LoadBalancerClient类型的bean
@ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(LoadBalancerRetryProperties.class)
public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration {
//所有被@LoadBalanced注解修饰的RestTemplate
@LoadBalanced
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RestTemplate> restTemplates = Collections.emptyList();
//对于所有被@LoadBalanced注解修饰的RestTemplate,
//调用SmartInitializingSingleton的customize方法
@Bean
public SmartInitializingSingleton loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializerDeprecated(
final ObjectProvider<List<RestTemplateCustomizer>> restTemplateCustomizers) {
return () -> restTemplateCustomizers.ifAvailable(customizers -> {
for (RestTemplate restTemplate : LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.this.restTemplates) {
for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
customizer.customize(restTemplate);
}
}
});
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public LoadBalancerRequestFactory loadBalancerRequestFactory(
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient) {
return new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancerClient, this.transformers);
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
static class LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig {
//产生一个LoadBalancerInterceptor类型的bean,包含loadBalancerClient类型的bean
@Bean
public LoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor(
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient,
LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) {
return new LoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, requestFactory);
}
//对于所有被@LoadBalanced注解修饰的RestTemplate,增加loadBalancerInterceptor属性
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(
final LoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) {
return restTemplate -> {
List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>(
restTemplate.getInterceptors());
list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor);
restTemplate.setInterceptors(list);
};
}
}
}
LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration配置类的作用是将所有被@LoadBalanced注解修饰的RestTemplate bean增LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器bean,而LoadBalancerInterceptor又包含loadBalancerClient,这样当用RestTemplate调用时,会首先调用拦截器方法,在拦截器方法里使用loadBalancerClient真正实现负载均衡以及url转换,达到服务名到真正的host之间的转换和负载均衡;
@LoadBalanced
使用该注解配置 RestTemplate Bean,通过注解源码可以看到,该注解的本质是一个 @Qualifier 注解。
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Qualifier
public @interface LoadBalanced {
}
Qualifier的意思是合格者,通过这个标示,表明了哪个实现类才是我们所需要的,添加@Qualifier注解,需要注意的是@Qualifier的参数名称为我们之前定义@Service注解的名称之一。
拦截器LoadBalancerInterceptor
public class LoadBalancerInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
private LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory;
public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer,
LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) {
this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer;
this.requestFactory = requestFactory;
}
//注入LoadBalancerClient 的实现 (唯一的实现就是RibbonLoadBalancerClient
public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) {
// for backwards compatibility
this(loadBalancer, new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancer));
}
//拦截
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body,
final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
//从请求url里面拿到服务名
final URI originalUri = request.getURI();
String serviceName = originalUri.getHost();
//LoadBalancerClient执行 根据服务名选择实例 发起请求 的过程
Assert.state(serviceName != null,
"Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri);
return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName,
this.requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution));
}
}
从代码可以看出 LoadBalancerInterceptor 拦截了请求后,通过LoadBalancerClient执行具体的请求发送。
LoadBalancerClient
LoadBalancerClient接口,有如下三个方法,其中excute()为执行请求,reconstructURI()用来重构url。
public interface LoadBalancerClient extends ServiceInstanceChooser {
//父接口方法
ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId);
<T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;
<T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance,
LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException;
URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original);
}
接口说明:
- ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId):根据传入的服务id,从负载均衡器中为指定的服务选择一个服务实例。
- T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest request):根据传入的服务id,指定的负载均衡器中的服务实例执行请求。
- T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest request):根据传入的服务实例,执行请求。
RibbonLoadBalancerClient
public class RibbonLoadBalancerClient implements LoadBalancerClient {
@Override
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request)
throws IOException {
return execute(serviceId, request, null);
}
public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request, Object hint)
throws IOException {
//获取负载均衡器
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId);
//负载均衡器ILoadBalancer根据负载均衡算法选取一个Server
Server server = getServer(loadBalancer, hint);
if (server == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId);
}
//
RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server,
isSecure(server, serviceId),
serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server));
return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request);
}
}
getLoadBalancer(serviceId)
- 获取负载均衡器
public class RibbonLoadBalancerClient implements LoadBalancerClient {
private SpringClientFactory clientFactory;
public RibbonLoadBalancerClient(SpringClientFactory clientFactory) {
this.clientFactory = clientFactory;
}
protected ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String serviceId) {
return this.clientFactory.getLoadBalancer(serviceId);
}
}
实际负载均衡的是通过 ILoadBalancer 来实现的。
public interface ILoadBalancer {
public void addServers(List<Server> newServers);
public Server chooseServer(Object key);
public void markServerDown(Server server);
@Deprecated
public List<Server> getServerList(boolean availableOnly);
public List<Server> getReachableServers();
public List<Server> getAllServers();
}
接口说明:
- addServers:向负载均衡器中添加一个服务实例集合。
- chooseServer:跟据key,从负载均衡器获取服务实例。
- markServerDown:用来标记某个服务实例下线。
- getReachableServers:获取可用的服务实例集合。
- getAllServers():获取所有服务实例集合,包括下线的服务实例。
ILoadBalancer 的实现 依赖关系示意图如下:
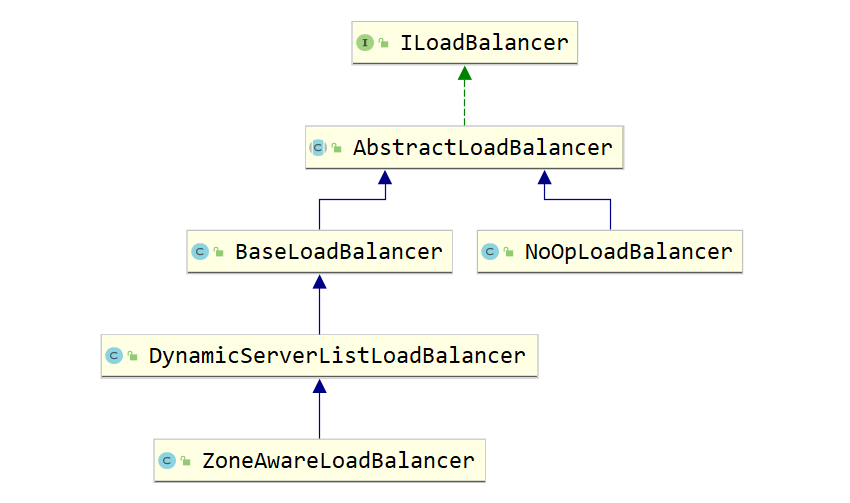
- NoOpLoadBalancer:啥都不做
- BaseLoadBalancer:
- 一个负载均衡器的基本实现,其中有一个任意列表,可以将服务器设置为服务器池。
- 可以设置一个ping来确定服务器的活力。
- 在内部,该类维护一个“all”服务器列表,以及一个“up”服务器列表,并根据调用者的要求使用它们。
- DynamicServerListLoadBalancer:
- 通过动态的获取服务器的候选列表的负载平衡器。
- 可以通过筛选标准来传递服务器列表,以过滤不符合所需条件的服务器。
- ZoneAwareLoadBalancer:
- 用于测量区域条件的关键指标是平均活动请求,它根据每个rest客户机和每个区域聚合。这是区域内未完成的请求总数除以可用目标实例的数量(不包括断路器跳闸实例)。当在坏区上缓慢发生超时时,此度量非常有效。
- 该负载均衡器将计算并检查所有可用区域的区域状态。如果任何区域的平均活动请求已达到配置的阈值,则该区域将从活动服务器列表中删除。如果超过一个区域达到阈值,则将删除每个服务器上活动请求最多的区域。一旦去掉最坏的区域,将在其余区域中选择一个区域,其概率与其实例数成正比。服务器将使用给定的规则从所选区域返回。对于每个请求,将重复上述步骤。也就是说,每个与区域相关的负载平衡决策都是实时做出的,最新的统计数据可以帮助进行选择。
RibbonClientConfiguration配置类可以看到,在整合Ribbon的时候Spring Cloud默认采用ZoneAwareLoadBalancer来实现负载均衡器。
@Import({ HttpClientConfiguration.class, OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class,
RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class, HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class })
public class RibbonClientConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}
}
从这段代码 ,也可以看出,负载均衡器所需的主要配置项是IClientConfig、ServerList、ServerListFilter、IRule、IPing、ServerListUpdater。
IClientConfig
IClientConfig 用于对客户端或者负载均衡的配置,它的默认实现类为 DefaultClientConfigImpl。
IRule
为LoadBalancer定义“负载均衡策略”的接口。
public interface IRule{
public Server choose(Object key);
public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb);
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();
}
IRule 的实现 依赖关系示意图如下:
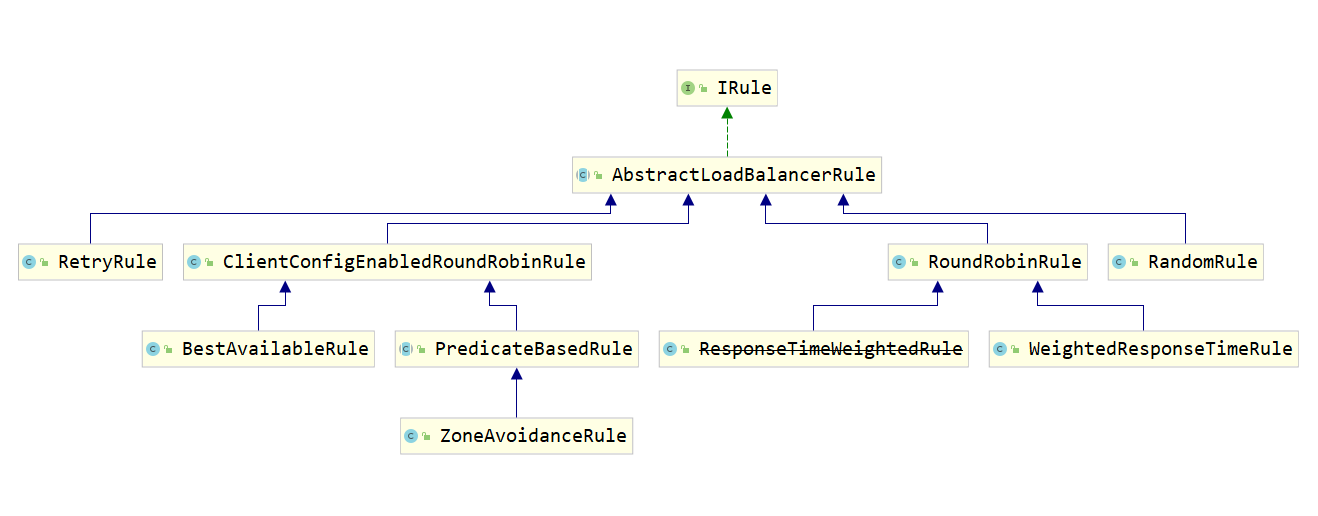
- BestAvailableRule:选择具有最低并发请求的服务器。
- ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule:轮询。
- RandomRule:随机选择一个服务器。
- RoundRobinRule:轮询选择服务器。
- RetryRule:具备重试机制的轮询。
- WeightedResponseTimeRule:根据使用平均响应时间去分配一个weight(权重) ,weight越低,被选择的可能性就越低。
- ZoneAvoidanceRule:根据区域和可用性筛选,再轮询选择服务器。
IPing
定义如何 “ping” 服务器以检查其是否存活。
public interface IPing {
public boolean isAlive(Server server);
}
IPing 的实现 依赖关系示意图如下:
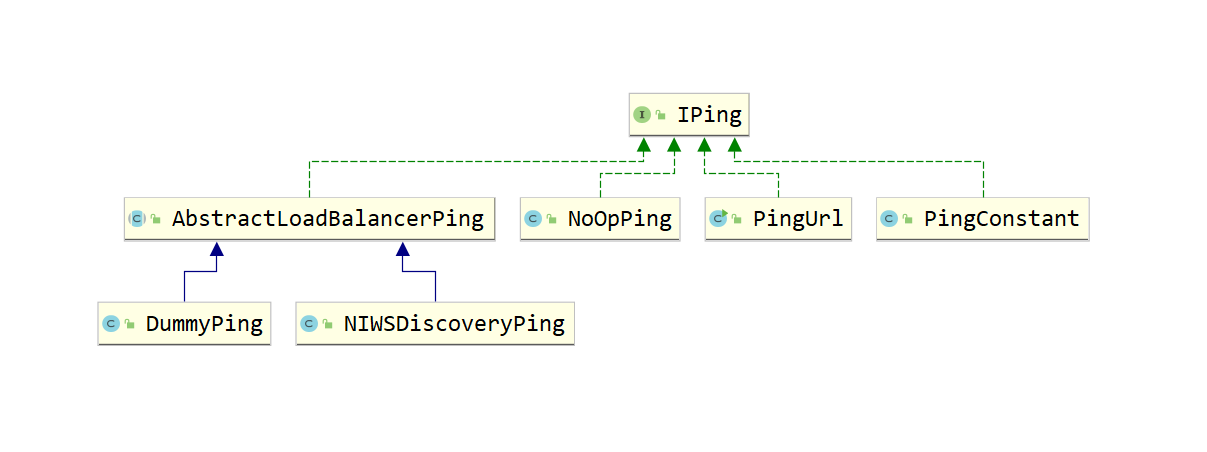
ServerList
定义获取所有的服务实例清单。
public interface ServerList<T extends Server> {
public List<T> getInitialListOfServers();
public List<T> getUpdatedListOfServers();
}
ServerList 的实现 依赖关系示意图如下:
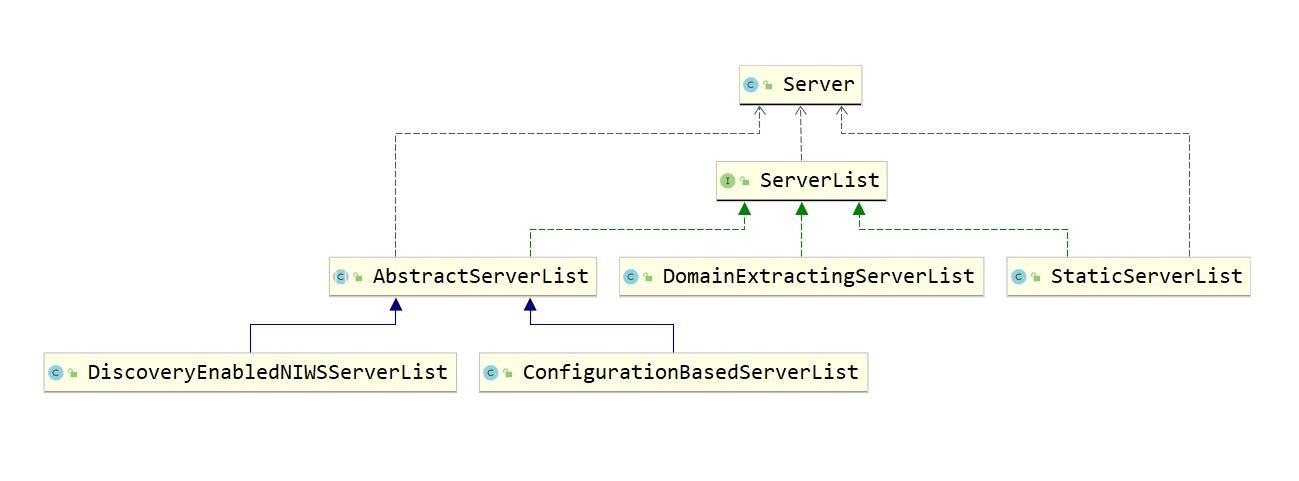
- DomainExtractingServerList:代理类,根据传入的ServerList的值,实现具体的逻辑。
- ConfigurationBasedServerList:从配置文件中加载服务器列表。
- DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList:从Eureka注册中心中获取服务器列表。
- StaticServerList:通过静态配置来维护服务器列表。
ServerListFilter
允许根据过滤配置动态获得的具有所需特性的候选服务器列表。
public interface ServerListFilter<T extends Server> {
public List<T> getFilteredListOfServers(List<T> servers);
}
ServerListFilter 的实现 依赖关系示意图如下:
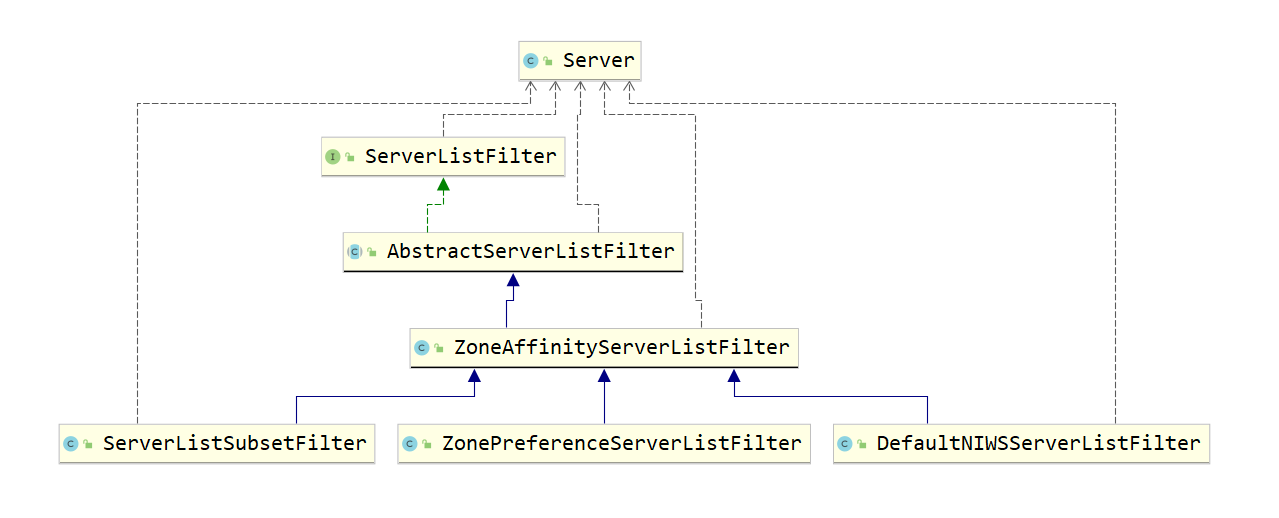
ServerListUpdater
用于执行动态服务器列表更新。
public interface ServerListUpdater {
public interface UpdateAction {
void doUpdate();
}
void start(UpdateAction updateAction);
void stop();
String getLastUpdate();
long getDurationSinceLastUpdateMs();
int getNumberMissedCycles();
int getCoreThreads();
}
ServerListUpdater 的实现 依赖关系示意图如下:
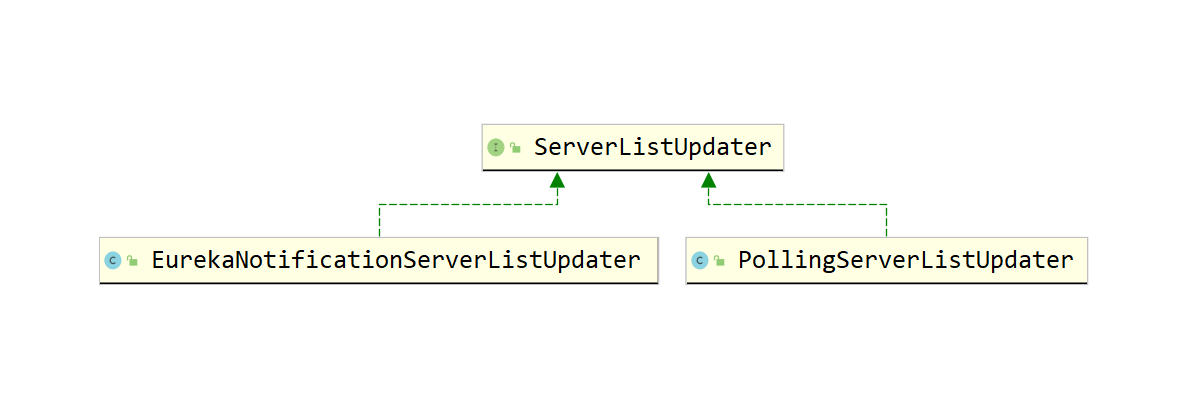
- PollingServerListUpdater:默认的实现策略,会启动一个定时线程池,定时执行更新策略。
- EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater:利用Eureka的事件监听器来驱动服务列表的更新操作。
getServer(loadBalancer, hint)
在RibbonLoadBalancerClient 中的execute方法调用getServer(loadBalancer, hint)方法,
即负载均衡器ILoadBalancer根据负载均衡算法选取一个Server。
public class RibbonLoadBalancerClient implements LoadBalancerClient {
protected Server getServer(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer, Object hint) {
if (loadBalancer == null) {
return null;
}
// Use 'default' on a null hint, or just pass it on?
return loadBalancer.chooseServer(hint != null ? hint : "default");
}
}
/**
* Ribbon负载均衡器的基础实现类
*/
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements
PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware {
//默认使用RoundRobinRule
private final static IRule DEFAULT_RULE = new RoundRobinRule();
protected IRule rule = DEFAULT_RULE;
//负载均衡的处理规则,默认使用RoundRobinRule规则,该规则实现了最基本且常用的线性负载均衡规则。
protected IRule rule = DEFAULT_RULE;
//检查服务实例操作时的执行策略对象,使用的策略是SerialPingStrategy
protected IPingStrategy pingStrategy = DEFAULT_PING_STRATEGY;
//用来检查服务实例是否正常,默认为null,需要在构造时注入它的具体实现
protected IPing ping = null;
//存储所有服务实例清单
@Monitor(name = PREFIX + "AllServerList", type = DataSourceType.INFORMATIONAL)
protected volatile List<Server> allServerList = Collections
.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>());
//存储正常服务实例清单
@Monitor(name = PREFIX + "UpServerList", type = DataSourceType.INFORMATIONAL)
protected volatile List<Server> upServerList = Collections
.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Server>());
//用来存储负载均衡器各服务实例属性和统计信息
protected LoadBalancerStats lbStats;
/*
* 负载均衡器实际将服务实例选择任务委托给了IRule实例中的choose函数来实现,挑选一个具体的服务实例
*/
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (counter == null) {
counter = createCounter();
}
counter.increment();
if (rule == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
return rule.choose(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e);
return null;
}
}
}
}
RoundRobinRule
Ribbon 默认的规则为 RoundRobinRule (轮询)
public class RoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
@Override
public Server choose(Object key) {
return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key);
}
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
log.warn("no load balancer");
return null;
}
Server server = null;
int count = 0;
//最多选择十次,就会结束尝试
while (server == null && count++ < 10) {
//获取所有可用的服务器
List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();
//获取所有服务器
List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers();
int upCount = reachableServers.size();
int serverCount = allServers.size();
if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) {
log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);
return null;
}
//获取下一个提供服务的下标
int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);
//获取指定下标的服务
server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex);
if (server == null) {
/* Transient. */
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) {
return (server);
}
// Next.
server = null;
}
//如果轮询次数Server超过10次,选择不到实例的话,会报警告信息。
if (count >= 10) {
log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: "
+ lb);
}
return server;
}
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) {
for (;;) {
//获取当前已有的请求总数
int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get();
//获取服务的下标
int next = (current + 1) % modulo;
//比较交换
if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next))
return next;
}
}
}
RibbonClientConfiguration
在Spring Cloud中,Ribbon默认的配置类是RibbonClientConfiguration。也可使用一个POJO自定义Ribbon的配置(自定义配置会覆盖默认配置)。这种配置是细粒度的,不同的Ribbon客户端可以使用不同的配置。
- 在SpringBoot启动类以外新建ribbonconfiguration包,并新建RibbonConfiguration类
/**
* @author: huangyibo
* @Date: 2019/11/2 18:08
* @Description: 如果将此类放进启动类的包下,那么此工程的所有ribbon都会使用这种负载均衡规则
*/
@Configuration
public class RibbonConfiguration {
//Ribbon提供的负载均衡策略
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule(){
return new RandomRule();
}
}
- Java代码配置
@Configuration
@RibbonClient(name="user-center",configuration = RibbonConfiguration.class)
public class UserCenterRibbonConfiguration {
}
- 用配置属性配置
# 通过配置文件指定user-center实例的ribbon负载均衡策略为RandomRule,和java代码方式指定效果一样
user-center:
ribbon:
NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule
RibbonClientConfiguration会初始化负载均衡器所需的主要配置项是IClientConfig、ServerList、ServerListFilter、IRule、IPing、ServerListUpdater并初始化ZoneAwareLoadBalancer。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@Import({ HttpClientConfiguration.class, OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class,
RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class, HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class })
public class RibbonClientConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IClientConfig ribbonClientConfig() {
DefaultClientConfigImpl config = new DefaultClientConfigImpl();
config.loadProperties(this.name);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout, DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout, DEFAULT_READ_TIMEOUT);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.GZipPayload, DEFAULT_GZIP_PAYLOAD);
return config;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IRule ribbonRule(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IRule.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IRule.class, config, name);
}
ZoneAvoidanceRule rule = new ZoneAvoidanceRule();
rule.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return rule;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IPing ribbonPing(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IPing.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IPing.class, config, name);
}
return new DummyPing();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ServerList<Server> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, name);
}
ConfigurationBasedServerList serverList = new ConfigurationBasedServerList();
serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return serverList;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerListUpdater ribbonServerListUpdater(IClientConfig config) {
return new PollingServerListUpdater(config);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ServerListFilter<Server> ribbonServerListFilter(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerListFilter.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerListFilter.class, config, name);
}
ZonePreferenceServerListFilter filter = new ZonePreferenceServerListFilter();
filter.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return filter;
}
}
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer的构造函数初始化父类DynamicServerListLoadBalancer
public class ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T> {
public ZoneAwareLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule,
IPing ping, ServerList<T> serverList, ServerListFilter<T> filter,
ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
super(clientConfig, rule, ping, serverList, filter, serverListUpdater);
}
}
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer {
public DynamicServerListLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping,
ServerList<T> serverList, ServerListFilter<T> filter,
ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
//初始化BaseLoadBalancer
super(clientConfig, rule, ping);
this.serverListImpl = serverList;
this.filter = filter;
this.serverListUpdater = serverListUpdater;
if (filter instanceof AbstractServerListFilter) {
((AbstractServerListFilter) filter).setLoadBalancerStats(getLoadBalancerStats());
}
restOfInit(clientConfig);
}
}
BaseLoadBalancer
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements
PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware {
public BaseLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config, IRule rule, IPing ping) {
initWithConfig(config, rule, ping, createLoadBalancerStatsFromConfig(config));
}
void initWithConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, IPing ping, LoadBalancerStats stats) {
this.config = clientConfig;
String clientName = clientConfig.getClientName();
this.name = clientName;
//初始化最长Ping间隔时间pingIntervalTime
int pingIntervalTime = Integer.parseInt(""
+ clientConfig.getProperty(
CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerPingInterval,
Integer.parseInt("30")));
//初始化最大Ping时间maxTotalPingTime
int maxTotalPingTime = Integer.parseInt(""
+ clientConfig.getProperty(
CommonClientConfigKey.NFLoadBalancerMaxTotalPingTime,
Integer.parseInt("2")));
setPingInterval(pingIntervalTime);
setMaxTotalPingTime(maxTotalPingTime);
setRule(rule);
setPing(ping);
setLoadBalancerStats(stats);
rule.setLoadBalancer(this);
if (ping instanceof AbstractLoadBalancerPing) {
((AbstractLoadBalancerPing) ping).setLoadBalancer(this);
}
logger.info("Client: {} instantiated a LoadBalancer: {}", name, this);
boolean enablePrimeConnections = clientConfig.get(
CommonClientConfigKey.EnablePrimeConnections, DefaultClientConfigImpl.DEFAULT_ENABLE_PRIME_CONNECTIONS);
//获取是否启用连接器验活标识enablePrimeConnections 默认为false。
//如果该值为true 会在加载的时候对使用所有服务器进行检测,
//通过PrimeConnections 来设置服务器的readyToServe 状态
if (enablePrimeConnections) {
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(true);
PrimeConnections primeConnections = new PrimeConnections(
this.getName(), clientConfig);
this.setPrimeConnections(primeConnections);
}
init();
}
public void setPingInterval(int pingIntervalSeconds) {
if (pingIntervalSeconds < 1) {
return;
}
this.pingIntervalSeconds = pingIntervalSeconds;
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("LoadBalancer [{}]: pingIntervalSeconds set to {}",
name, this.pingIntervalSeconds);
}
//设置Server的定时Ping任务
setupPingTask(); // since ping data changed
}
}
- 初始化最长Ping间隔时间pingIntervalTime和最大Ping时间maxTotalPingTime 没有地方使用到。
- setPingInterval调用setupPingTask方法,启动Ping任务
- 获取是否启用连接器验活标识enablePrimeConnections 默认为false。如果该值为true 会在加载的时候对使用所有服务器进行检测,通过PrimeConnections 来设置服务器的readyToServe 状态
setupPingTask
- 设置Server的定时Ping任务
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements
PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware {
protected int pingIntervalSeconds = 10;
void setupPingTask() {
if (canSkipPing()) {
return;
}
// 如果已经有了定时任务,则取消
if (lbTimer != null) {
lbTimer.cancel();
}
// 第二个参数为true,表示它是一个deamon线程
lbTimer = new ShutdownEnabledTimer("NFLoadBalancer-PingTimer-" + name,
true);
// 创建 PingTask, 它继承于 TimerTask,定时执行 run 方法
// 启动PingTask任务,每10秒执行一次
lbTimer.schedule(new PingTask(), 0, pingIntervalSeconds * 1000);
forceQuickPing();
}
}
PingTask 任务
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements
PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware {
private final static SerialPingStrategy DEFAULT_PING_STRATEGY = new SerialPingStrategy();
protected IPingStrategy pingStrategy = DEFAULT_PING_STRATEGY;
class PingTask extends TimerTask {
public void run() {
try {
// 默认 pingStrategy = new SerialPingStrategy()
new Pinger(pingStrategy).runPinger();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error pinging", name, e);
}
}
}
class Pinger {
public void runPinger() throws Exception {
// 如果正在ping,则返回
if (!pingInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return; // Ping in progress - nothing to do
}
// 所有的服务,包括不可用的服务
Server[] allServers = null;
boolean[] results = null;
Lock allLock = null;
Lock upLock = null;
try {
/*
* The readLock should be free unless an addServer operation is
* going on...
*/
allLock = allServerLock.readLock();
allLock.lock();
allServers = allServerList.toArray(new Server[allServerList.size()]);
allLock.unlock();
// 所有服务的数量
int numCandidates = allServers.length;
// 所有服务ping的结果
results = pingerStrategy.pingServers(ping, allServers);
// 状态可用的服务列表
final List<Server> newUpList = new ArrayList<Server>();
// 状态改变的服务列表
final List<Server> changedServers = new ArrayList<Server>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCandidates; i++) {
// 最新的状态
boolean isAlive = results[i];
Server svr = allServers[i];
// 老的状态
boolean oldIsAlive = svr.isAlive();
// 更新状态
svr.setAlive(isAlive);
// 如果状态改变了,则放到集合中,会进行重新拉取
if (oldIsAlive != isAlive) {
changedServers.add(svr);
logger.debug("LoadBalancer [{}]: Server [{}] status changed to {}",
name, svr.getId(), (isAlive ? "ALIVE" : "DEAD"));
}
// 状态可用的服务
if (isAlive) {
newUpList.add(svr);
}
}
upLock = upServerLock.writeLock();
upLock.lock();
upServerList = newUpList;
upLock.unlock();
// 变态改变监听器
notifyServerStatusChangeListener(changedServers);
} finally {
// ping 完成
pingInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}
}
pingServers检测服务的状态
public class BaseLoadBalancer extends AbstractLoadBalancer implements
PrimeConnections.PrimeConnectionListener, IClientConfigAware {
private static class SerialPingStrategy implements IPingStrategy {
// 检测服务的状态
@Override
public boolean[] pingServers(IPing ping, Server[] servers) {
int numCandidates = servers.length;
boolean[] results = new boolean[numCandidates];
logger.debug("LoadBalancer: PingTask executing [{}] servers configured", numCandidates);
for (int i = 0; i < numCandidates; i++) {
results[i] = false; /* Default answer is DEAD. */
try {
if (ping != null) {
results[i] = ping.isAlive(servers[i]);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Exception while pinging Server: '{}'", servers[i], e);
}
}
return results;
}
}
}
Ribbon 每10秒向 EurekaClient 发送 ping 来判断服务的可用性,如果服务的可用性发生了改变或服务的数量和之前的不一致,则会更新或重新拉取服务。有了这些服务之后,会根据负载均衡策略 IRule 来选择一个可用的服务。
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer#restOfInit(clientConfig)
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer {
void restOfInit(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
boolean primeConnection = this.isEnablePrimingConnections();
// turn this off to avoid duplicated asynchronous priming done in BaseLoadBalancer.setServerList()
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(false);
//定时更新Eureka Client实例列表
enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature();
//获取所有Eureka Client实例列表
updateListOfServers();
if (primeConnection && this.getPrimeConnections() != null) {
this.getPrimeConnections()
.primeConnections(getReachableServers());
}
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(primeConnection);
LOGGER.info("DynamicServerListLoadBalancer for client {} initialized: {}", clientConfig.getClientName(), this.toString());
}
}
enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature()
- 每30秒定时更新Eureka Client实例列表
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer {
public void enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature() {
LOGGER.info("Using serverListUpdater {}", serverListUpdater.getClass().getSimpleName());
serverListUpdater.start(updateAction);
}
}
public class PollingServerListUpdater implements ServerListUpdater {
//更新服务实例在初始化之后延迟1秒后开始执行
private static long LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_UPDATE_DELAY = 1000; // msecs;
//以30秒为周期重复执行
private static int LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_REPEAT_INTERVAL = 30 * 1000; // msecs;
//以定时任务的方式进行服务列表的更新。
@Override
public synchronized void start(final UpdateAction updateAction) {
if (isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
//创建一个Runnable的线程wrapperRunnable
final Runnable wrapperRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!isActive.get()) {
if (scheduledFuture != null) {
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
}
return;
}
try {
//具体更新服务实例列表的方法
updateAction.doUpdate();
lastUpdated = System.currentTimeMillis();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Failed one update cycle", e);
}
}
};
//为wrapperRunnable线程启动一个定时任务
scheduledFuture = getRefreshExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(
wrapperRunnable,
initialDelayMs, //1秒
refreshIntervalMs, //30秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
);
} else {
logger.info("Already active, no-op");
}
}
}
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer {
public DynamicServerListLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
this.isSecure = false;
this.useTunnel = false;
this.serverListUpdateInProgress = new AtomicBoolean(false);
class NamelessClass_1 implements UpdateAction {
NamelessClass_1() {
}
public void doUpdate() {
//获取所有Eureka Client的服务实例列表
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.this.updateListOfServers();
}
}
this.updateAction = new NamelessClass_1();
this.initWithNiwsConfig(clientConfig);
}
}
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer#updateListOfServers()
- 获取所有Eureka Client实例列表
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer {
@VisibleForTesting
public void updateListOfServers() {
List<T> servers = new ArrayList();
if (this.serverListImpl != null) {
//实现从Eureka Server中获取服务可用实例列表
servers = this.serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}", this.getIdentifier(), servers);
if (this.filter != null) {
servers = this.filter.getFilteredListOfServers((List)servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}", this.getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
//更新服务实例列表
this.updateAllServerList((List)servers);
}
}
public class DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList extends AbstractServerList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>{
@Override
public List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> getUpdatedListOfServers(){
return obtainServersViaDiscovery();
}
private List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> obtainServersViaDiscovery() {
List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> serverList = new ArrayList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>();
if (eurekaClientProvider == null || eurekaClientProvider.get() == null) {
logger.warn("EurekaClient has not been initialized yet, returning an empty list");
return new ArrayList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>();
}
EurekaClient eurekaClient = eurekaClientProvider.get();
if (vipAddresses!=null){
for (String vipAddress : vipAddresses.split(",")) {
// if targetRegion is null, it will be interpreted as the same region of client
//从DiscoveryClient中的localRegionApps中获取服务实例缓存列表
List<InstanceInfo> listOfInstanceInfo = eurekaClient.getInstancesByVipAddress(vipAddress, isSecure, targetRegion);
for (InstanceInfo ii : listOfInstanceInfo) {
if (ii.getStatus().equals(InstanceStatus.UP)) {
if(shouldUseOverridePort){
if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.debug("Overriding port on client name: " + clientName + " to " + overridePort);
}
// copy is necessary since the InstanceInfo builder just uses the original reference,
// and we don't want to corrupt the global eureka copy of the object which may be
// used by other clients in our system
InstanceInfo copy = new InstanceInfo(ii);
if(isSecure){
ii = new InstanceInfo.Builder(copy).setSecurePort(overridePort).build();
}else{
ii = new InstanceInfo.Builder(copy).setPort(overridePort).build();
}
}
DiscoveryEnabledServer des = createServer(ii, isSecure, shouldUseIpAddr);
serverList.add(des);
}
}
if (serverList.size()>0 && prioritizeVipAddressBasedServers){
break; // if the current vipAddress has servers, we dont use subsequent vipAddress based servers
}
}
}
return serverList;
}
}
@Singleton
public class DiscoveryClient implements EurekaClient {
private final AtomicReference<Applications> localRegionApps = new AtomicReference<Applications>();
private volatile Map<String, Applications> remoteRegionVsApps = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public List<InstanceInfo> getInstancesByVipAddress(String vipAddress, boolean secure,
@Nullable String region) {
if (vipAddress == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Supplied VIP Address cannot be null");
}
Applications applications;
if (instanceRegionChecker.isLocalRegion(region)) {
//获取服务实例缓存列表
applications = this.localRegionApps.get();
} else {
//获取服务实例缓存列表
applications = remoteRegionVsApps.get(region);
if (null == applications) {
logger.debug("No applications are defined for region {}, so returning an empty instance list for vip "
+ "address {}.", region, vipAddress);
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
if (!secure) {
return applications.getInstancesByVirtualHostName(vipAddress);
} else {
return applications.getInstancesBySecureVirtualHostName(vipAddress);
}
}
}
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer#updateAllServerList
public class DynamicServerListLoadBalancer<T extends Server> extends BaseLoadBalancer {
protected void updateAllServerList(List<T> ls) {
if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
for (T s : ls) {
// 状态设置为可用
s.setAlive(true);
}
//设置服务实例列表
setServersList(ls);
// 强制检测服务状态
super.forceQuickPing();
} finally {
serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}
@Override
public void setServersList(List lsrv) {
//将服务实例列表设置到父类(BaseLoadBalancer)的allServerList中
super.setServersList(lsrv);
List<T> serverList = (List<T>) lsrv;
Map<String, List<Server>> serversInZones = new HashMap<String, List<Server>>();
for (Server server : serverList) {
getLoadBalancerStats().getSingleServerStat(server);
String zone = server.getZone();
if (zone != null) {
zone = zone.toLowerCase();
List<Server> servers = serversInZones.get(zone);
if (servers == null) {
servers = new ArrayList<Server>();
serversInZones.put(zone, servers);
}
servers.add(server);
}
}
setServerListForZones(serversInZones);
}
}
正如名所示,DynamicServerListLoadBalancer可以动态的加载后端服务列表,DynamicServerListLoadBalancer中使用一个ServerListRefreshExecutorThread任务线程定期的更新后端服务列表。
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/huanchupkblog/p/10923229.html
https://blog.csdn.net/u014494148/article/details/108915053
https://my.oschina.net/mengyuankan/blog/3104184
 架构C
架构C